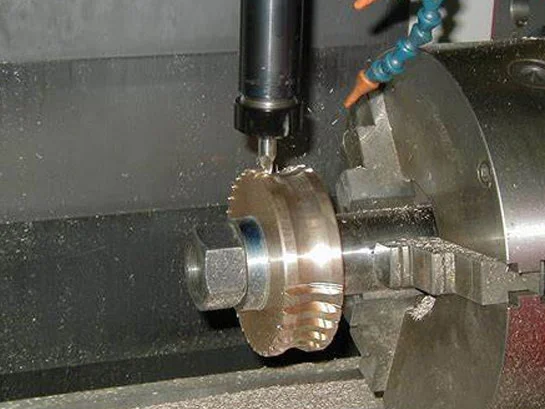
4 axis custom CNC machining service provided for the prototype manufacturing of high precision and quality mechanical parts such as sprial shaft and gear as well as complex components for both metal and plastic.
For your next 4-axis CNC milling job, team up with Fathom Precision's creative aerospace professionals. We are a dependable prototyping company of high-performance complicated aircraft components because of our extensive superalloy expertise and understanding of the aerospace industry. For your 4-axis milling needs, get in touch with us right now.

A 4 axis CNC machined part refers to a component that has been produced using a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine that has the capability to rotate around four different axes. These machines supplied by 4 axis cnc machining factory are capable of producing parts with a high degree of precision and accuracy in custom CNC service.

The main feature of a 4 axis CNC machined part is its ability to be produced with a greater level of complexity and precision than other manufacturing processes. This is due to the ability of the CNC machine to rotate around four different axes, allowing for a more intricate design to be produced. Additionally, 4 axis CNC machines are often able to produce parts at a faster rate than other machines, which can make them a more cost-effective custom prototype manufacturing solution.

4 axis CNC machining parts are used in a wide range of applications, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronics. They are often used in applications where a high degree of precision is required, such as in the production of complex shapes, intricate designs, and tight tolerances.

Some of the main advantages of using 4 axis CNC machining to produce parts include the ability to produce complex designs with a high degree of precision and accuracy, the ability to produce parts at a faster rate than other machines, and the ability to produce parts with a high level of consistency and repeatability. Additionally, 4 axis CNC machining can often be more cost-effective than other manufacturing processes, especially for larger production runs.
4-axis and 5-axis machining refer to the number of directions in which a cutting tool can move during the machining process. The difference between the two lies in the complexity of the parts they can produce and the precision of the machining.
4-Axis Machining: In 4-axis machining, the cutting tool can move in four directions: X, Y, Z, and A axis (rotation around the X-axis). This allows the machine to perform more complex operations than a 3-axis machine, such as cutting around the sides of a workpiece or creating holes on a slant. However, the workpiece still needs to be manually repositioned for machining from different angles.
5-Axis Machining: In 5-axis CNC machining, the cutting tool can move in five directions: X, Y, Z, A, and B axis (rotation around the Y-axis). This allows the machine to cut the workpiece from almost any angle in a single setup, enabling the production of more complex and intricate parts. 5-axis machines can also produce parts with higher precision and better surface finish than 4-axis machines.
While 4-axis machining offers more capabilities than 3-axis machining, 5-axis machining provides even greater flexibility and precision, allowing for the production of more complex parts and reducing the need for multiple setups.
The process of 4-axis CNC machining involves several steps:
Designing the Part: The first step in the process is to design the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design is then converted into a format that the CNC machine can understand, typically using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software.
Setting Up the Machine: The next step is to set up the CNC machine. This involves installing the appropriate cutting tool in the machine and setting the origin point for the machining process.
Loading the Program: The program created by the CAM software is then loaded into the CNC machine. This program controls the movements of the machine during the machining process.
Securing the Workpiece: The workpiece is then secured in the machine using a fixture or vise. It’s crucial to ensure that the workpiece is properly aligned with the machine’s axes.
Machining the Part: Once everything is set up, the machining process can begin. The machine follows the program, moving the cutting tool along the X, Y, Z, and A axes to cut the workpiece. The A axis allows for rotation around the X axis, enabling the machine to cut the workpiece from different angles.
Checking the Part: After the machining process is complete, the part is checked to ensure it meets the required specifications. This may involve measuring the part or inspecting it visually.
Finishing: Depending on the requirements of the part, it may need to be finished. This could involve processes like sanding, polishing, or coating the part to improve its appearance or durability.
Quality Control: Finally, the part undergoes a quality control process to ensure it meets all the required standards and specifications.
4-Axis CNC machines are used in a variety of industries due to their ability to produce complex and precise parts. Here are some of the key applications:
Automotive Industry: 4-axis CNC machines are used to manufacture various automotive parts such as engine components, gears, and other complex parts that require high precision.
Aerospace Industry: These machines are used to create parts for aircraft and spacecraft, including turbine parts, airfoils, and other complex shapes that require precise machining from various angles.
Medical Industry: 4-axis CNC machines are used to create medical devices and components, such as surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and parts for diagnostic equipment.
Electronics Industry: These machines are used to manufacture parts for electronic devices, such as circuit boards, connectors, and casings.
Woodworking: 4-axis CNC machines are used in woodworking to create intricate designs and patterns on wooden parts.
Jewelry Industry: These machines are used to create intricate designs and patterns on jewelry pieces.
Mold and Die Making: 4-axis CNC machines are used to create molds and dies for various industries, including plastic injection molding and metal casting.
Prototyping: These machines are often used for prototyping, as they can quickly and accurately produce complex parts from a variety of materials.
Engraving: 4-axis CNC machines can be used for engraving complex patterns on various surfaces.
Increased Complexity: 4-axis CNC machining allows for the creation of more complex parts than 3-axis machining. The additional axis allows the machine to rotate the workpiece, enabling cuts from multiple angles without having to reposition the workpiece manually.
Improved Efficiency: Because the workpiece can be cut from multiple angles in a single setup, 4-axis machining can reduce the time and effort required to produce a part, increasing overall efficiency.
Enhanced Precision: 4-axis CNC machines can produce parts with high precision and consistency, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring that every part meets the required specifications.
Greater Flexibility: 4-axis CNC machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, providing greater flexibility in the types of parts that can be produced.
Reduced Waste: By automating the machining process, 4-axis CNC machines can reduce waste by ensuring that cuts are made accurately and efficiently.
Cost-Effective: Although the initial investment in a 4-axis CNC machine may be higher than for a 3-axis machine, the increased efficiency and precision can lead to cost savings in the long run.
Versatility: 4-axis CNC machines are used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, and more, making them a versatile tool for any manufacturing operation.
This video serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of this advanced machining process, which is instrumental in creating complex and precision parts used in various industries.
4 Axis CNC Machining is a sophisticated manufacturing process that involves a computer numerical control (CNC) machine with four axes of motion. This allows for more complex shapes and designs to be machined with high precision and consistency, which would be impossible with traditional machining methods.